什么是MVC,什么是Spring MVC
MVC(Model View Controller)是一种软件设计规范,是一种将业务逻辑、数据、显示分离的一种解耦思想。由模型(Model)处理应用程序的数据部分,视图(View)处理数据显示部分,它们两者之间交友控制器(Controller)调度,控制器通常从视图读取数据,控制用户输入,并向模型发送数据。而Spring MVC是由Spring提供的遵循MVC的规范的轻量级web框架,目的是为了简化Java栈的web开发。
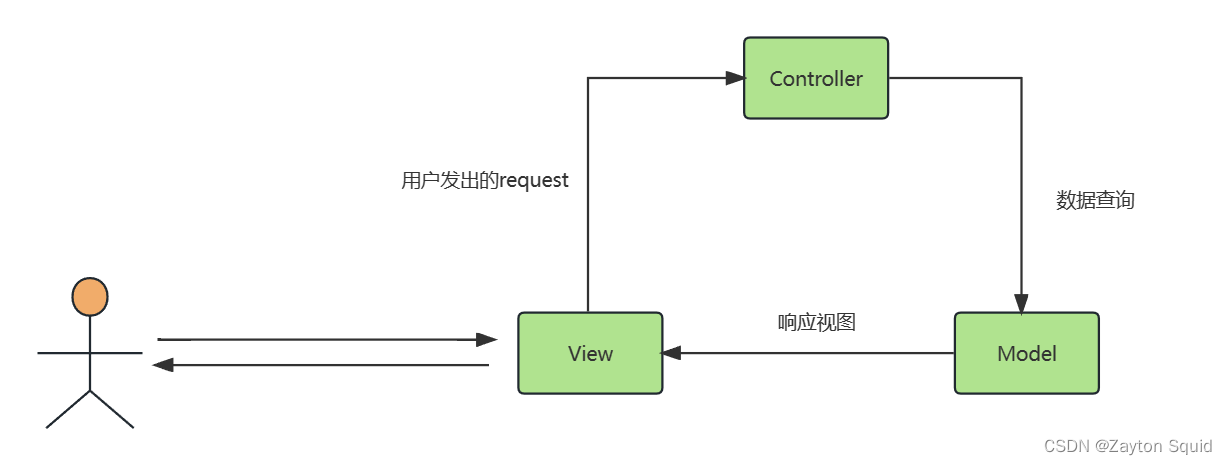
Spring MVC 的核心组件
DispatcherServlet:前端控制器,负责接收分发用户请求,并给予客户端响应。HandlerMapping:处理器映射器,根据URL去找到合适的Handler。HandlerAdapter:处理器适配器,根据HandlerMapping找到的Handler,适配执行对应的Handler。Handler:处理器,处理用户的请求。ViewResovler:视图解析器,根据Handler返回的结果,解析并渲染成对应的页面,然后传递给DispatcherServlet返回给前端。
SpringMVC工作原理是什么
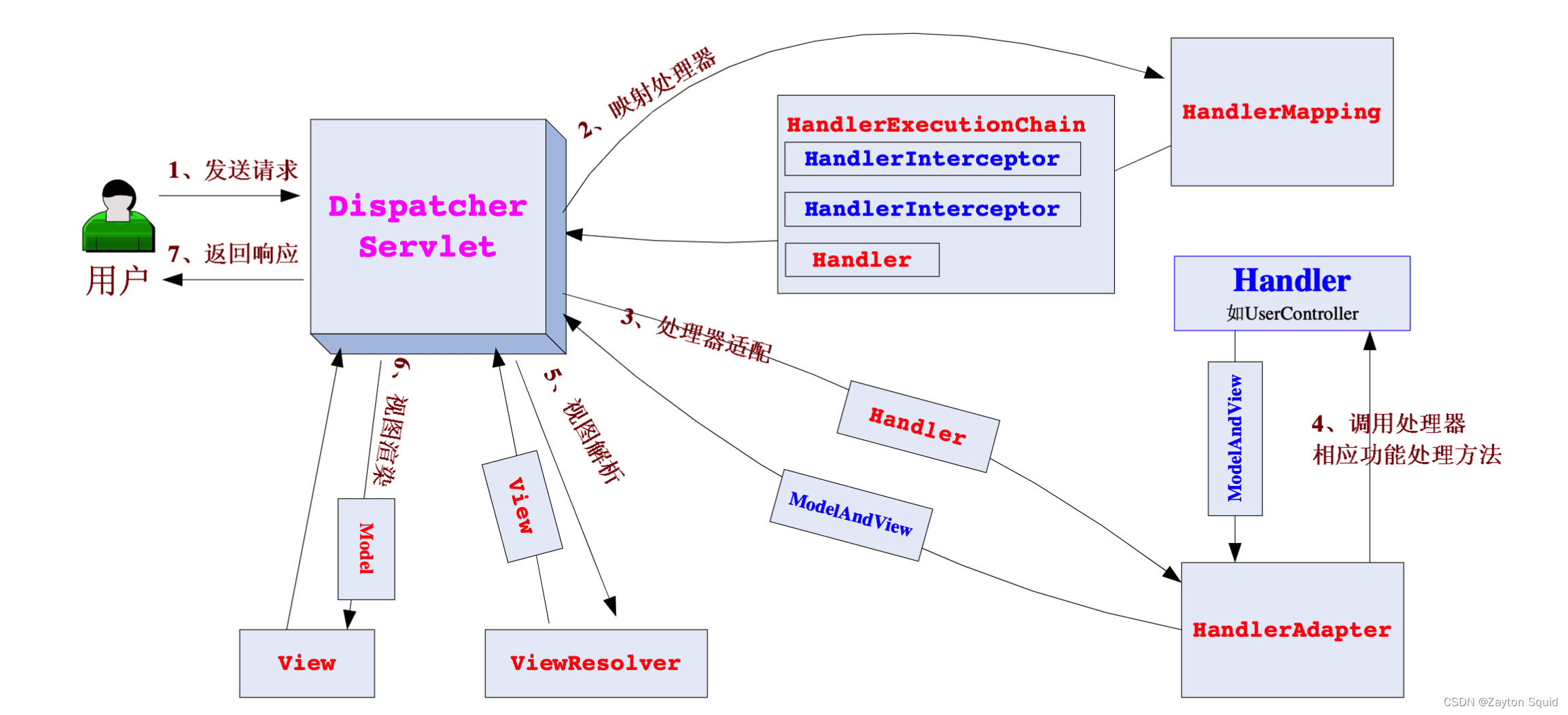
- 用户向服务器发送请求,请求被
DispatcherServlet拦截。 DispatcherServlet根据信息找到对应的HandlerMapping。- 通过
HandlerMapping找到具体的处理器(Controller或Handler)和拦截器,生成处理器对象及处理器拦截器并返回给DispatcherServlet。 - 然后
DispatcherServlet调用HanlderAdapter处理器适配器执行对应的Handler。 Handler完成对用户请求的处理后,会返回一个ModelAndView给DispatcherServlet。DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView传给ViewReslover视图解析器。ViewReslover解析后返回具体的view给DispatcherServlet。DispatcherServlet根据view进行渲染视图(即将Model数据填充至视图),然后响应给用户。
源码分析
搭建Spring MVC的示例代码
maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>>5.3.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>taglibs</groupId>
<artifactId>standard</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency>
Controller层
@Controller
public class HelloController {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloController.class);
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public ModelAndView hello(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
logger.info("hello方法 被调用");
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("message", "Hello World!");
modelAndView.setViewName("index");
return modelAndView;
}
}
配置springmvc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<!-- 扫描注解 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="org.springmvc"/>
<!-- 静态资源处理 -->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
<!-- 开启注解 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<!-- 视图解析器 -->
<bean id="jspViewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="viewClass" value="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView"/>
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
</beans>
配置web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1">
<!-- 定义Spring MVC的前端控制器 -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!-- 通过初始化参数指定SpringMVC配置文件的位置和名称 -->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
编写jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>welcome</title>
</head>
<body>
${requestScope.message}
</body>
</html>
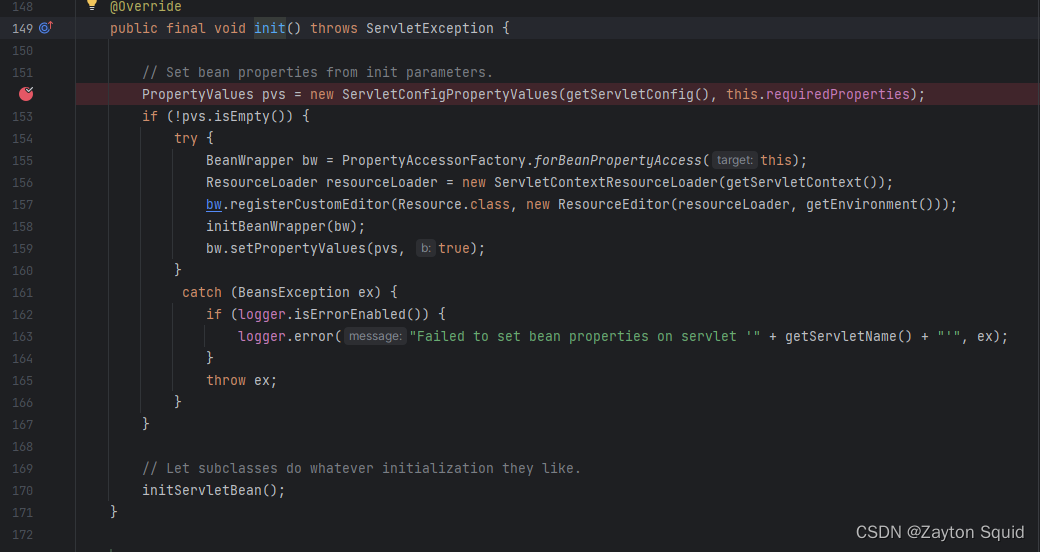
DispatcherServlet初始化过程
启动tomcat后,找到init()的方法位于HttpServletBean中,打上断点,开始进行分析
 在
在HttpServletBean#init中,init()主要读取web.xml中servlet参数配置,并将交给子类方法initServletBean()继续初始化
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// 获得web.xml中的contextConfigLocation配置属性,就是spring MVC的配置文件
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
// 转换成BeanWrapper,为了方便使用Spring的属性注入功能
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
// 获取服务器的各种信息
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
// 更多的初始化可以让子类去拓展
initBeanWrapper(bw);
// 让spring注入namespace,contextConfigLocation等属性
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// 让子类去拓展
initServletBean();
}
从下图中可以看到web.xml中的servlet参数配置被读取。
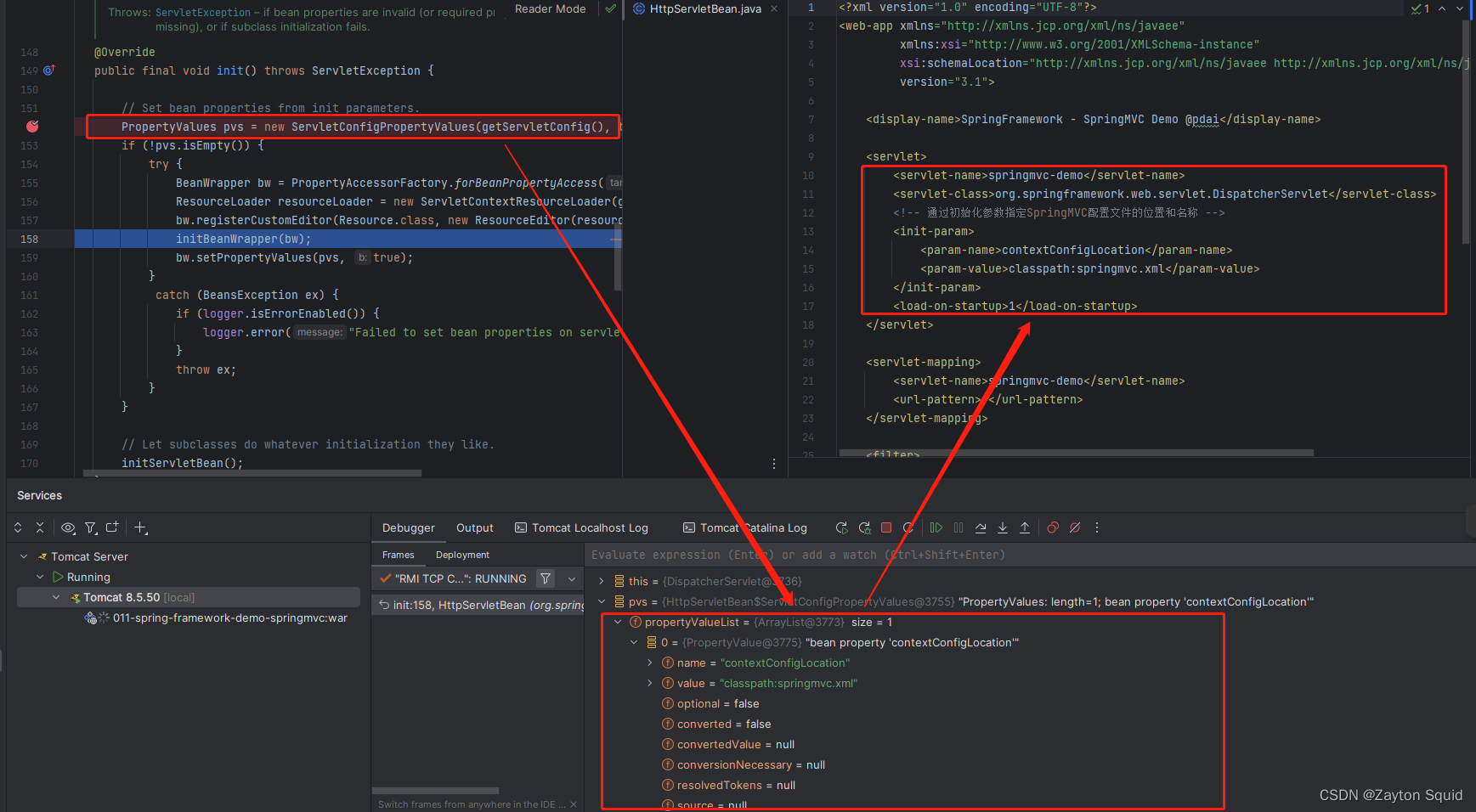 再看下
再看下FrameworkServlet#initServletBean()方法。
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 最重要的是这个方法
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
// 可以让子类进一步拓展
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
//忽略....
}
initWebApplicationContext用来初始化和刷新WebApplicationContext
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
// 如果在构造函数已经被初始化
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
// 没有在构造函数中初始化,则尝试通过contextAttribute初始化
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
// 还没有的话,只能重新创建了
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
webApplicationContext只会初始化一次,依次尝试构造函数初始化,没有则通过findWebApplicationContext()方法初始化,仍没有则使用createWebApplicationContext()创建新的,下面我们看看createWebApplicationContext的源码。
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
//忽略...
// 通过反射方式初始化
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
//获取springmvc.xml
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
//初始化上下文,设置id,environment,configLocation
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法初始化上下文
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
// 设置context ID
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
// 设置servletContext, servletConfig, namespace, listener...
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
// 让子类去拓展
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
// Spring环境初始化完了,就可以初始化DispatcherServlet处理流程中需要的组件了。
wac.refresh();
}
webApplicationContext创建完成后,我们返回到FrameworkServlet#initWebApplicationContext,执行onRefresh()方法,调用initStrategies(context)方法对DispatcherServlet中的组件进行初始化,这些组件就是在SpringMVC请求流程中包的主要组件。
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
//initHandlerxx 重点
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
在initHandlerMappings中,它默认会加载所有HandlerMapping然后根据优先级进行排序,优先使用优先级高的HandlerMapping;若想加载指定HandlerMapping则在web.xml中将detectAllHandlerMappings设置为false,Spring MVC就只会查找名为handlerMapping的bean,并作为当前系统的唯一的HandlerMapping
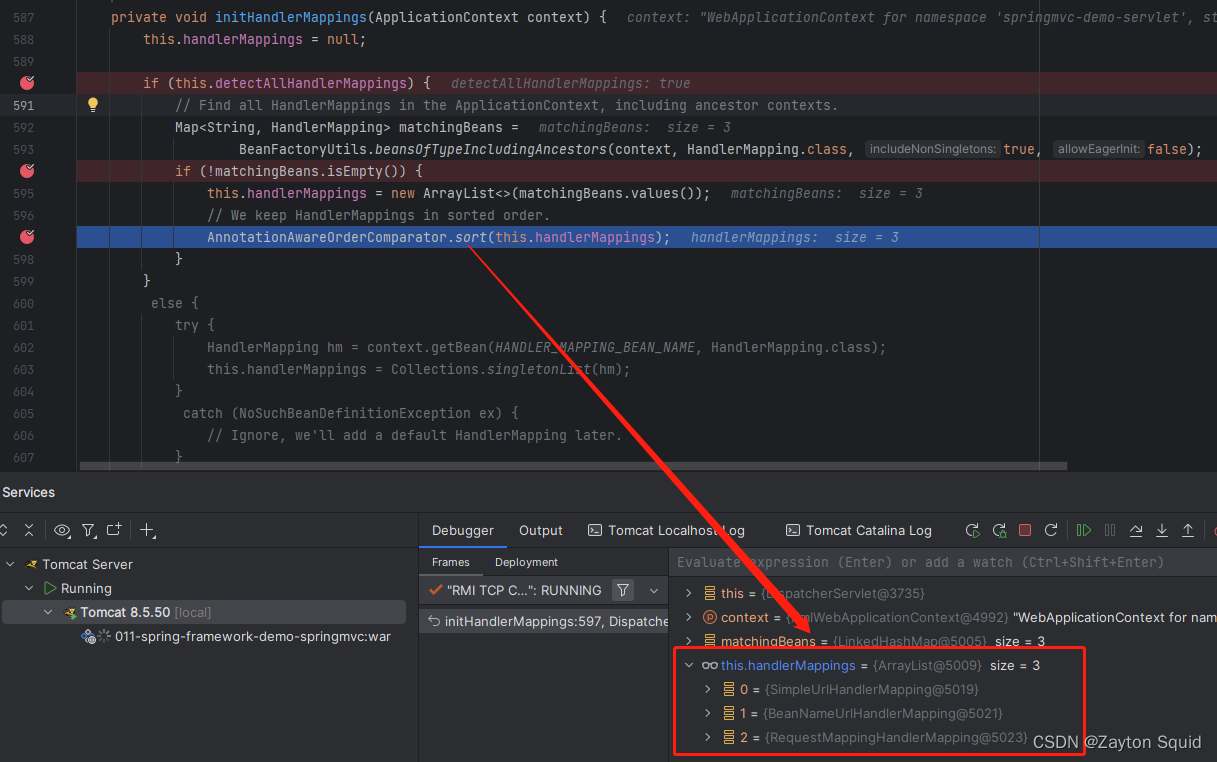
initHandlerAdapters方法和initHandlerExceptionResolvers方法与initHandlerMappings是相似的。
DispatcherServlet处理请求的过程
客户端发送请求给服务器端,服务器端会将请求发送给Servlet,然后Servlet初始化就是上文所述的阶段,Servlet在执行期间会调用HttpServlet的service()的方法,该方法会判断客户端的请求方式,不同请求方式调用不同的方法,假设我们的请求是get,那么它就会调用doGet。我们在DispatcherServlet的父类FrameworkServlet 找到重写HttpServlet的service()方法,所以我们从FrameworkServlet#service开始分析。
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());
//请求方法是patch或者为null,则
if (httpMethod == HttpMethod.PATCH || httpMethod == null) {
processRequest(request, response);
}
else {
super.service(request, response);
}
}
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = req.getMethod();
//如果请求方式是Get
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
//忽略....
}
}
//忽略....
}
判断请求方式是Get后,会进入到doGet方法,然后执行processRequest处理请求
@Override
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//忽略....
// 初始化context
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
// 看这里
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
//忽略....
}
}
然后执行DispatcherServlet#doService方法
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// 保存下请求之前的参数.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
//忽略....
}
// 方便后续 handlers 和 view 要使用它们.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
//忽略....
}
RequestPath previousRequestPath = null;
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
previousRequestPath = (RequestPath) request.getAttribute(ServletRequestPathUtils.PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
ServletRequestPathUtils.parseAndCache(request);
}
try {
// 看这里,终于将这个请求分发出去了
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
//忽略...
}
}
DispatcherServlet的doDispatch就会找到合适的HandlerMapping交由适配器找到合适的handler进行包装然后着手处理
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
// 判断是不是文件上传类型的request
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 根据handlerMapping找到合适的handler.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 根据handler获取匹配的handlerAdapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
//忽略....
// handle执行并返回一个modelAndView
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
// 通过视图的prefix和postfix获取完整的视图名
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 应用后置的拦截器
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
//忽略...
// 处理handler处理的结果,该结果要么是ModelAndView,要么是要解析为ModelAndView的异常。
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
//忽略...
}
在AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter#handle中会交给handleInternal方法处理
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
checkRequest(request);
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
//获取session
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
//上锁,执行处理逻辑,得到modelAndView
synchronized (mutex) {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}
执行invokeHandlerMethod对RequestMapping处理程序方法
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
// 获取ModelFactory,ModelFactory可以协助控制器在调用方法之前初始化模型,并在调用之后更新模型
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
//设置handler方法上的参数
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
// 尝试绑定参数、返回值解析器
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
// 创建ModelAndViewContainer,并初始化Model对象
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
// 异步请求相关
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);
asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {
Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult();
mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0];
asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found concurrent result value [" + result + "]");
}
invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result);
}
// 执行Controller中的具体方法并处理返回值
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
// 返回ModelAndView对象
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
finally {
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}
而后直接来到InvocableHandlerMethod#doInvoke
//使用给定的参数值调用处理程序方法。
protected Object doInvoke(Object... args) throws Exception {
Method method = getBridgedMethod();
try {
if (KotlinDetector.isSuspendingFunction(method)) {
return CoroutinesUtils.invokeSuspendingFunction(method, getBean(), args);
}
//执行Control类中的方法
return method.invoke(getBean(), args);
}
//忽略....
}
然后回到processDispatchResult方法对视图和模型进行处理,最后将结果返回给DispatcherServlet,由DispatcherServlet响应给用户。
过滤器和拦截器的区别
我们不妨基于一段示例代码来了解一下二者的区别,首先我们在项目中配置过滤器,直接实现Filter接口即可,也可以通过注解@WebFilter来实现。
@Component
public class MyFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("Filter 前置");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("Filter 处理中");
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("Filter 后置");
}
}
拦截器则通过实现HandlerInterceptor接口
@Component
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Interceptor 前置");
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Interceptor 处理中");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Interceptor 后置");
}
}
拦截器编写好后,还需要配置一些属性设置才使得拦截器能拦截所有URL。
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new MyInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**");
}
}
配置完拦截器后,我们访问下面这条命令,就会看到上面拦截器和过滤器输出的信息。
curl http://localhost:8080/hello
实现原理不同
过滤器的工作原理是基于函数回调的,将一个个过滤器组成一个过滤器链,以责任链模式的方式在请求到达web容器时,按顺序一个一个执行filter,例如我们上面请求hello方法时,请求就会依次调用Spring MVC中的ApplicationFilterChain走到MyFilter。
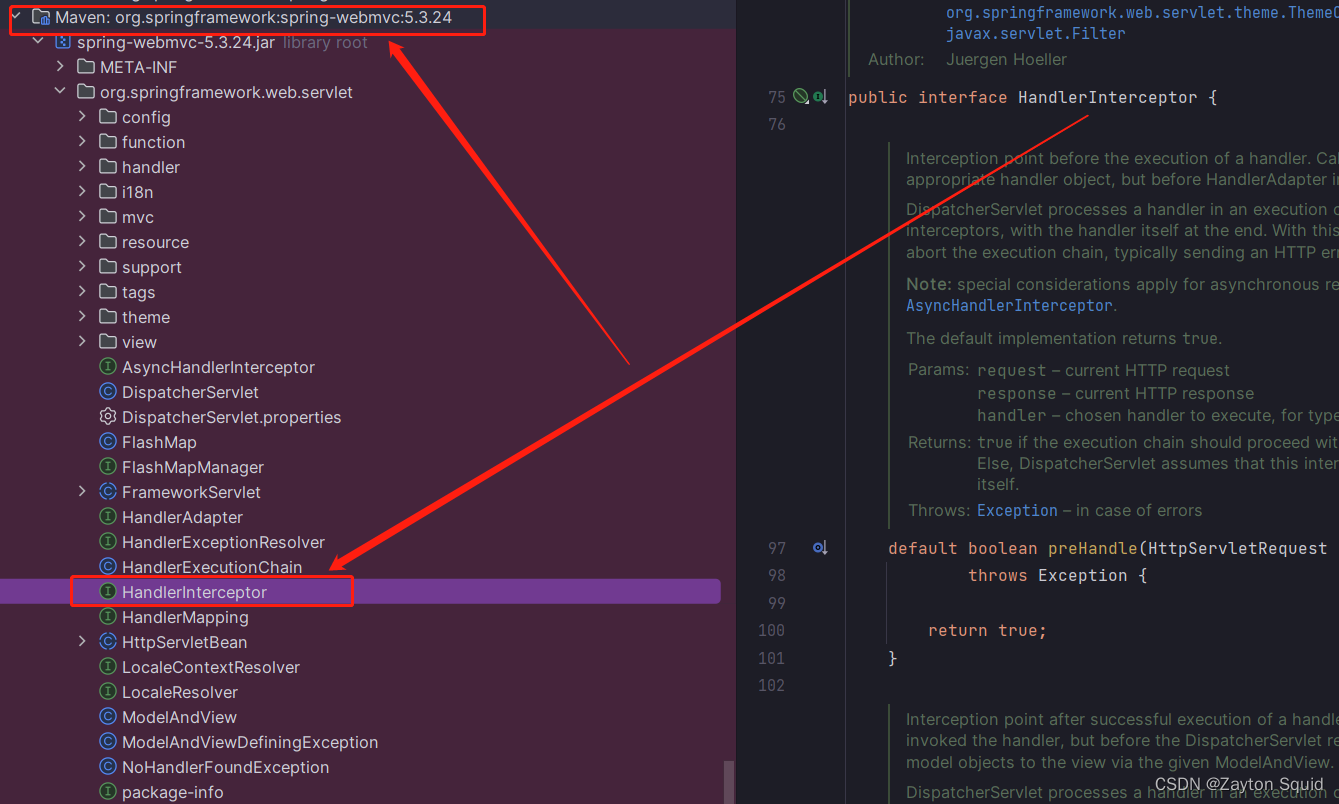
我们直接deBug的方式更直观的了解,如下图所示,根据堆栈信息我们可以看到最初访问的是ApplicationFilterChain的doFilter方法
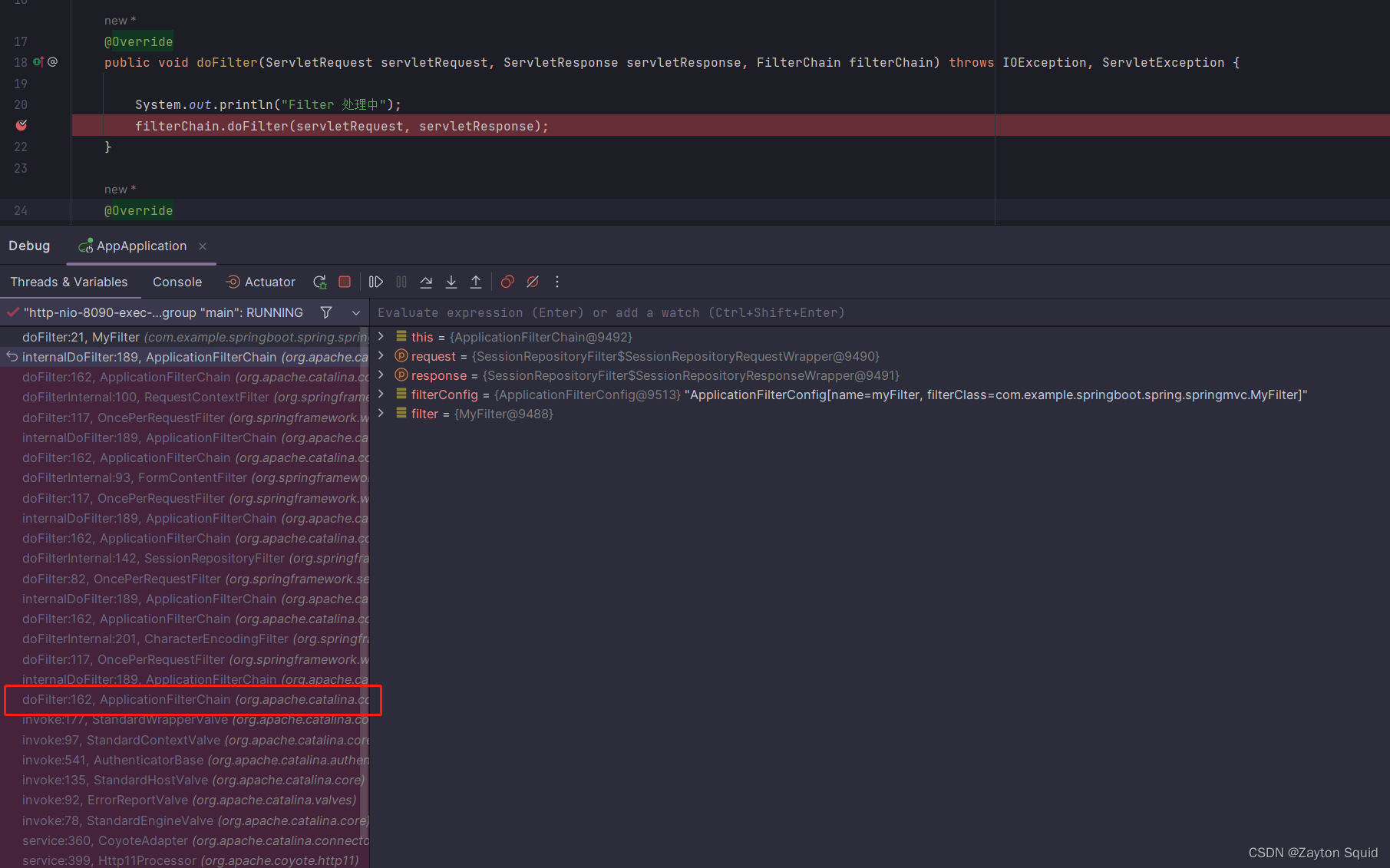 点进
点进doFilter方法可以看到它会执行internalDoFilter方法,获取第pos个filter,然后执行 filter.doFilter(request, response, this);。
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
//忽略...
} else {
internalDoFilter(request,response);
}
}
private void internalDoFilter(ServletRequest request,
ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (pos < n) {
//获取第pos个filter
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = filters[pos++];
try {
Filter filter = filterConfig.getFilter();
if (request.isAsyncSupported() && "false".equalsIgnoreCase(
filterConfig.getFilterDef().getAsyncSupported())) {
//忽略.......
} else {
//执行下一个过滤器的filter逻辑
filter.doFilter(request, response, this);
}
}
//忽略.......
return;
}
//忽略.......
而拦截器则是基于Java的反射机制(动态代理)实现的。
使用范围不同
从源码中我们可以看到过滤器是依赖于Tomcat等容器,导致它只能作用于web程序。
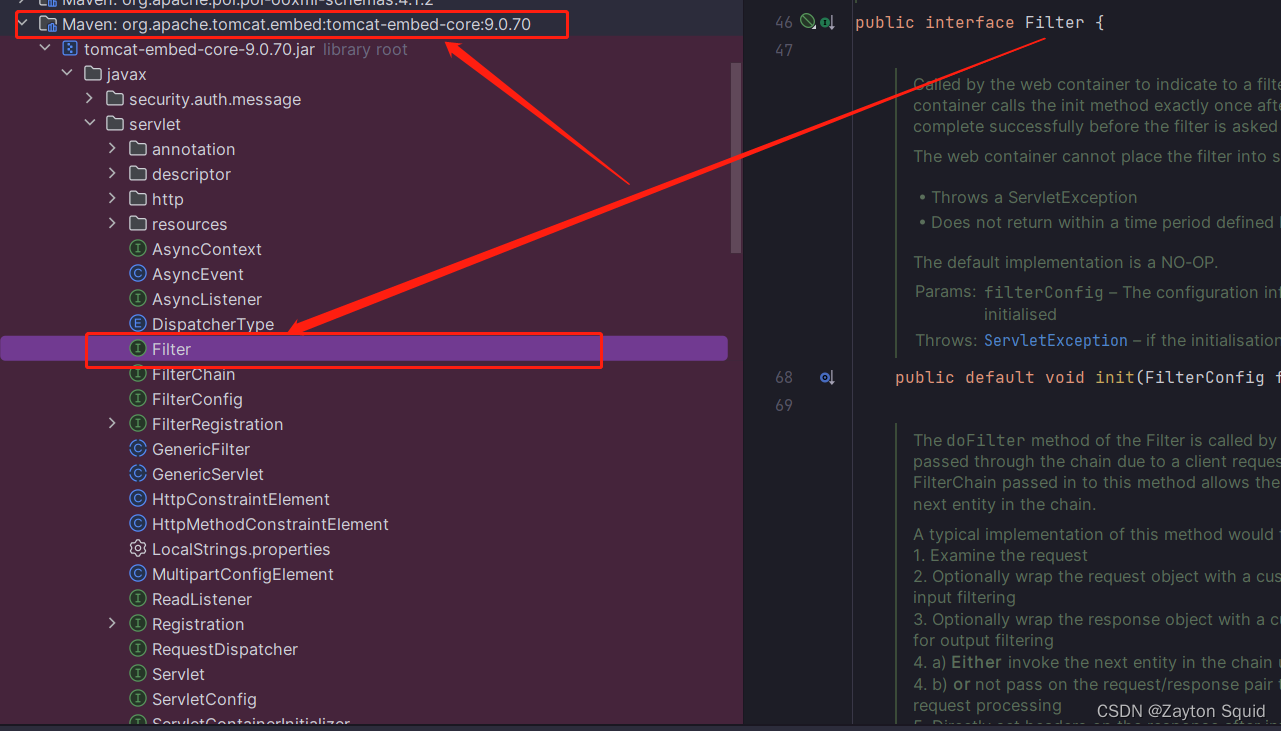 而
而拦截器是一个Spring组件,由Spring容器,这就说明它可以单独使用,不仅能应用与web程序,还可以用于application或swing等程序。
执行顺序不同
上文请求后可以看到控制台输出下面这一段结果
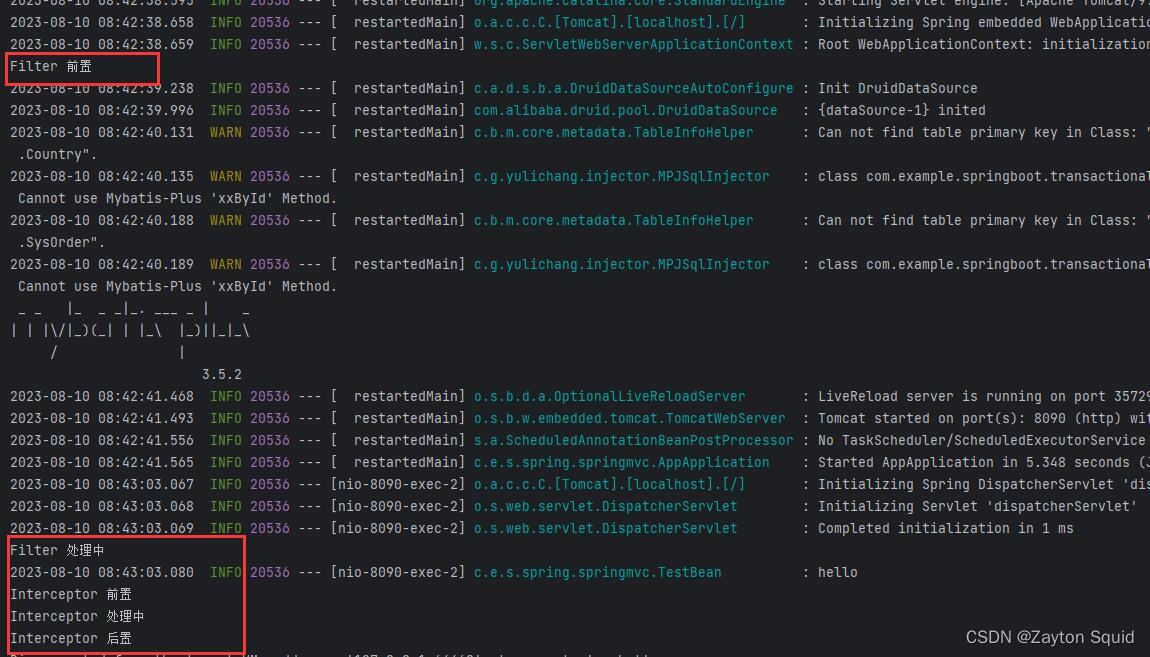
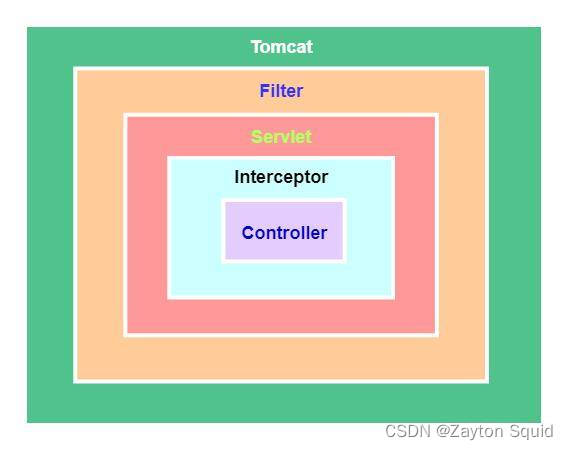
可以看出web请求是先经过过滤器,然后再到达拦截器的,它们的执行顺序如下图所示:
注入Bean情况不同
下面我们分别在过滤器和拦截器中注入bean,看看有什么区别。
@Component
public class TestBean {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TestBean.class);
public void hello(){
logger.info("hello");
}
}
在过滤器中注入bean
@Component
public class MyFilter implements Filter {
@Autowired
private TestBean testBean;
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("Filter 处理中");
testBean.hello();
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);
}
......
}
然后再拦截器中也注入bean
@Component
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Autowired
private TestBean testBean;
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Interceptor 前置");
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
testBean.hello();
System.out.println("Interceptor 处理中");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Interceptor 后置");
}
}
然后启动项目,发送请求,发现居然报了空指针,原因是拦截器是在spring context之前加载的,所以在它创建时,我们自定的bean还没有生成。
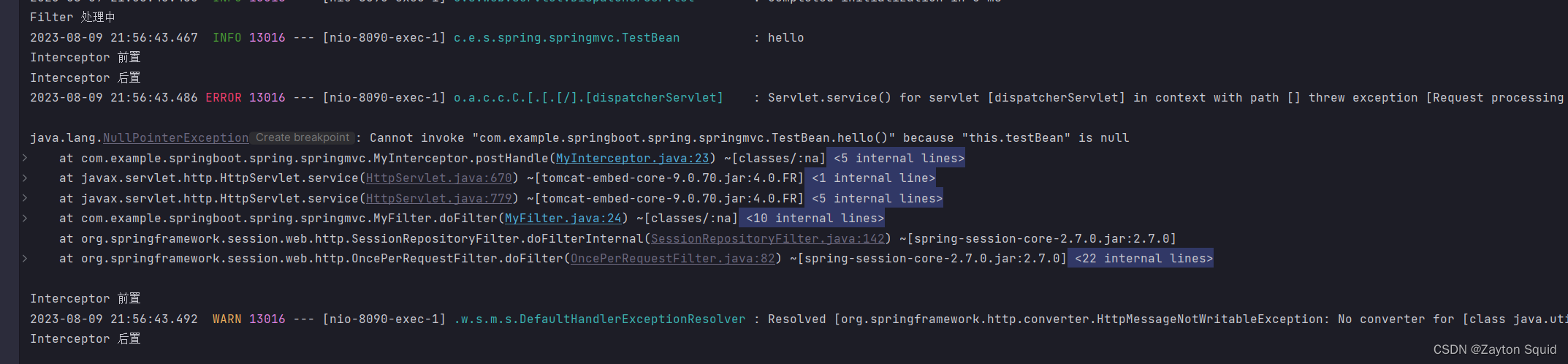 那么解决方案也很简单,就是在注册拦截器之前,先将
那么解决方案也很简单,就是在注册拦截器之前,先将Interceptor 手动注入。
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Bean
public MyInterceptor getMyInterceptor(){
return new MyInterceptor();
}
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(getMyInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**");
}
}
调整顺序的方式不同
过滤器直接在类上用@Order控制执行顺序,值越小优先级越高,而拦截器则是在addInterceptors方法中使用order方法调整顺序。
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(getMyInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**").order(1);
}
有一点需要注意,当有多个拦截器时,先声明的拦截器preHandle()方法先执行,而postHandle()方法反而会后执行。这一点我们从源码中可以看出来,在DispatcherServlet的doDispatch方法中,在执行applyPreHandle的地方,我们看执行逻辑可以看出它的for循环是正序的,也就是说拦截器的applyPreHandle方法是顺序执行的,而applyPostHandle的for循环是反向的,这就明白为什么postHandle()、preHandle() 执行顺序是相反的了。
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
try {
//忽略.....
try {
// 获取可以执行当前Handler的适配器
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 注意: 执行Interceptor中PreHandle()方法,是正向for循环依次执行
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 注意:执行Handle【包括我们的业务逻辑,当抛出异常时会被Try、catch到】
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 注意:执行Interceptor中PostHandle方法是反向for循环依次执行【抛出异常时无法执行】
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
}
//忽略.....
}
参考文献
https://www.pdai.tech/md/spring/spring-x-framework-springmvc-source-1.html
https://www.pdai.tech/md/spring/spring-x-framework-springmvc-source-2.html